
Interactions | Reactions | Processes
Classified as: Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle
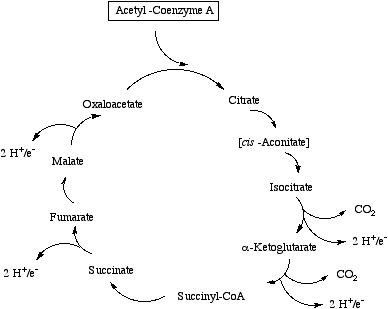
The tricarboxylic acid (or citric acid) cycle involves the conversion of acetyl coenzyme A into carbon dioxide, protons and electrons.
+ |
+ |
Citrate Synthase |
+ |
CoA–SH |
+ |
Aconitase |
+ |
H2O |
+ |
H2O |
+ |
Aconitase |
+ |
Isocitrate Dehydrogenase |
+ |
2 |
H• |
+ |
Isocitrate Dehydrogenase |
+ |
CO2 |
+ |
CoA–SH |
+ |
α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase |
+ |
CO2 |
+ |
2 |
H• |
+ |
GDP |
+ |
[PO4]3– |
+ |
Succinyl-CoA Synthetase |
+ |
GTP |
+ |
CoA–SH |
+ |
Succinate Dehydrogenase |
+ |
2 |
H• |
+ |
H2O |
+ |
Fumarase |
+ |
Malate Dehydrogenase |
+ |
2 |
H• |
© Mark R. Leach 1999 –
Queries, Suggestions, Bugs, Errors, Typos...
If you have any:
Queries
Comments
Suggestions
Suggestions for links
Bug, typo or grammatical error reports about this page,please contact Mark R. Leach, the author, using mark@meta-synthesis.com