
Interactions | Reactions | Processes
Classified as: Ambidentate Enolate Ions 1
According to Pearsons hard soft [Lewis] acid base principle, hard Lewis acids have a strong affinity for hard Lewis bases and soft Lewis acids have a strong affinity for soft Lewis bases.
Enolate ions have a hard alkoxide ion end which preferentially complexes with hard Lewis acids such as Li+, and a soft nucleophilic carbanion end displaces soft iodide ion from methyl iodide and soft bromide ion from Br2.Note that while hard vs soft comparisons can be made for carefully selected pairs of species and/or reactive centres, the HSAB analysis is NOT general. For more information look in the Chemogenesis webbook section on Pearson's HSAB principle.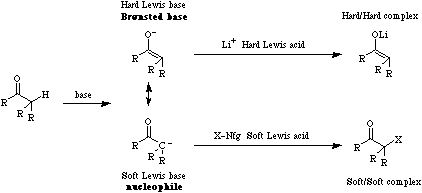
Li+ |
+ |
+ |
CH3I |
+ |
I– |
+ |
Br2 |
© Mark R. Leach 1999 –
Queries, Suggestions, Bugs, Errors, Typos...
If you have any:
Queries
Comments
Suggestions
Suggestions for links
Bug, typo or grammatical error reports about this page,please contact Mark R. Leach, the author, using mark@meta-synthesis.com