
Interactions | Reactions | Processes
Classified as: Ambidentate Behaviour: Elimination vs Substitution 2
According to Pearsons hard soft [Lewis] acid base principle, hard Lewis acids have a strong affinity for hard Lewis bases and soft Lewis acids have a strong affinity for soft Lewis bases.
Hard alkoxide ion preferentially abstracts a hard proton, so initiating E2 elimination, whereas soft nucleophilic malonate carbanion preferentially displaces soft bromide ion nucleofuge. (Note that the pKa values of the conjugate acids, ethanol and diethyl malonate, a similar, around 16.) Note that while hard vs soft comparisons can be made for carefully selected pairs of species and/or reactive centres, the HSAB analysis is NOT general. For more information look in the Chemogenesis webbook section on Pearson's HSAB principle.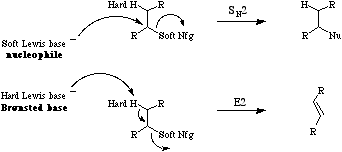
(CH3)2CHBr |
+ |
+ |
Br– |
(CH3)2CHBr |
+ |
CH3CH2O– |
CH3–CH=CH2 |
+ |
Br– |
+ |
CH3CH2OH |
© Mark R. Leach 1999 –
Queries, Suggestions, Bugs, Errors, Typos...
If you have any:
Queries
Comments
Suggestions
Suggestions for links
Bug, typo or grammatical error reports about this page,please contact Mark R. Leach, the author, using mark@meta-synthesis.com